- When is Data Migration Needed?
- Six Types of Data Migration
- Tips to Consider Before Data Migration
- Data Migration Approaches
- Stages of a Data Migration Plan
- Building Migration Solution
- Mitigating the Risk Factors in Data Migration
- Difference between Data Migration, Data Integration, and Data Conversion
Data migration is the process of transferring data from one system to another, and it's a critical aspect of many business operations. We'll explore what data migration is, its benefits, and some common use cases.
Here are the key takeaways from the article:
- Data migration involves moving data from one system to another while maintaining data integrity and accuracy.
- There are several benefits to data migration, including increased efficiency, improved data security, and enhanced data quality.
- Some common use cases for data migration include system upgrades, cloud migration, and merging data from multiple systems.
- A successful data migration requires careful planning, a thorough understanding of the source and target systems, and effective testing and validation processes.
- Choosing the right data migration tool and working with experienced professionals can help ensure a smooth and successful data migration process.
In the article, we'll delve deeper into each of these points and provide more information on the benefits and use cases of data migration, as well as some best practices for ensuring a successful migration.
Introduction
Data migration, as the name suggests, refers to a multi-step process of transferring data from one application, file format, or storage system to another. With enterprise organizations producing ever-increasing amounts of data, it has become imperative to select environments that can optimally store this data to amplify the value extracted from it.
Generally, data migration involves decommissioning legacy systems by mapping data to new systems. Today, a common use case of this is migrating on-premises data systems and infrastructure to cloud-based environments as more and more companies are investing huge sums to cut storage costs and boost productivity. As per survey results from different sectors, only an estimated 16% of the data migration projects are successfully delivered within the stipulated time and budget because of the complexity and constraints involved in the process.
In this article, we will deep-dive into different types of data migration, the stages of a data migration plan, as well as the risks associated with the data migration process and how they can be mitigated.
When is Data Migration Needed?
While overhauling old systems and replacing them altogether is often the most common cause, businesses undertake data migrations for a variety of other reasons as well:
- Upgrading database management systems or database schemas as databases expand in size and demand greater storage capacity
- Opting to shift to cloud computing environments from physical, on-premises systems
- Consolidating different data sources after corporate mergers or acquisitions
- Upgrades in existing hardware, applications, and file formats
- Archiving and removing data that is not useful anymore
- Establishing new data warehouses or data lakes for analytics and reporting purposes
- Curtailing operational costs by reducing the number of data hosting systems
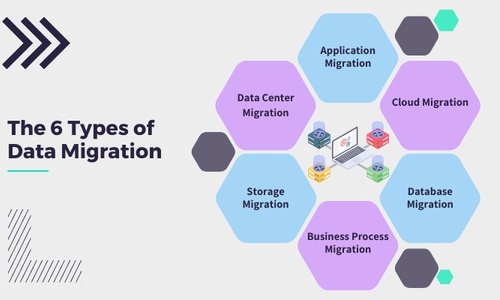
The 6 Types of Data Migration
There are six major types of data migration and an individual data migration plan can include multiple types from the following:
Data Center Migration
Data Center Migration refers to moving the data center infrastructure to a new physical or cloud-based location. A data center houses network routers, storage devices, server systems, and other critical infrastructural equipment of an organization.
Application Migration
Application Migration is when data related to certain applications has to be transferred to a new computing environment. This could involve shifting entire applications from a local server to a cloud storage or between two different cloud environments or moving just the underlying data in case of a software upgrade at the provider’s end. This type of migration is especially complex because applications interact with other programs. Problems typically arise because source systems and target systems have unique data formats and models. Enterprise software vendors usually provide special APIs to the companies to maintain data integrity during the migration process.
Cloud Migration
Cloud Migration is related to the relocation of data, business apps, and services from one cloud environment to another or from an on-site data center to a cloud-based one. This is one of the most popular types of data migration and it allows enterprises to scale more effectively, access resources more readily, and trim overheads related to the physical management of on-premises infrastructure. According to Gartner, more than 45% of IT spending on infrastructure management, business process outsourcing, and application software will move from traditional to cloud computing solutions by 2024.
Database Migration
Database Migration becomes necessary when organizations have to shift to a different database vendor, upgrade the database management software, or migrate the database to a cloud provider’s environment. Typically, it could mean either updating to a new version of the same database management system or shifting to a new database management system offered by a different service provider such as migrating from Oracle to PostgreSQL.
Business Process Migration
Business Process Migration refers to the movement of business data, processes, and applications to a new environment. This could include the transfer of databases and programs relating to business operations, products, and customer experiences. The driving factors of this type of migration are business reorganization, acquisitions, and mergers to realign goals or target new markets.
Storage Migration
Storage Migration is the process of migrating data from one storage medium to another. A common use case of this migration is when companies need to do away with traditional storage equipment like hard-disk drives and move the data to more durable and faster storage devices such as solid-state drives. Storage migration does not change the underlying data formats and it enables companies to not only achieve significantly faster performance but also ensure more effective data backup and data validation.
Tips to Consider Before Data Migration
Data migration, if executed correctly, can prove to be extremely beneficial for companies. Listed below are some points that companies can keep in consideration before migration. These can help in ensuring a smooth and painless data migration process but also in augmenting its positive impact on the business:
- Conducting pre-migration assessment of the existing system. This will help in better understanding the structure of the underlying system as well as in setting business goals for the migration.
- Analyzing performance statistics of the old infrastructural resources such as data storage systems, databases, and application programs. This will give an idea of user requirements and will also help in setting performance benchmarks for post-migration optimization.
- Review specifications of the physical and virtual assets of the company such as storage configurations, number of CPUs etcetera. This will assist in drafting a budget and preventing avoidable costs.
- Another way of preventing unwanted expenses is by segmenting servers according to their business requirement and by using the correct servers for the workloads on which the migration is happening.
- Data migration is a continuous process and future migrations are unavoidable. Therefore, it is important for the higher-ups in an organization to utilize resources appropriately and apply best practices to ensure effective data migration.
Data Migration Approaches
There are two major approaches to data migration. While planning and implementation depend on the type of migration chosen, it is also imperative to choose the right data migration process as per the requirements of the business. The two approaches are detailed below:
Big Bang Migration
Big Bang Migration is when all data assets and associated services and programs are migrated from the source system to the target system in one operation within a set window. Its implementation strategy requires all systems to be unavailable for usage throughout the migration service. Therefore, companies usually execute big bang migrations during public vacations when system usage is not needed.
The advantages of this migration approach are that it is cost-effective and also less time-consuming as all transformations happen in a single operation. Companies do not have to contend with running old and new systems at the same time. However, the downside of this approach is that there is a high risk of migration failure due to big data disrupting transmission processes. This could also result in data loss in situations where proper backups are not assured. Therefore, big bang migrations are generally utilized by small-sized companies or in those cases where the data to be transmitted is not overwhelming in size.
Trickle Migration
Trickle Migration, on the other hand, is a phased migration approach. Also known as iterative migration, it partitions the migration process into smaller migrations. The transfer of data from the source system to the target system happens in a phase-wise manner and each of these sub-processes has its own execution timelines.
In this way, no downtime is required during the migration process because the old system can remain in operation alongside the new system while the migration service is on-going. This migration approach is also less prone to failures because if any sub-process confronts an unexpected error, only that sub-process needs to be re-run rather than redoing the whole migration again. However, trickle migrations tend to be much more complicated because of their iterative nature. They are also more expensive in terms of time and resource consumption because they require both old and new systems to function simultaneously. This migration approach is usually used by large-scale enterprises that cannot afford downtime across the entire system during migration.
Stages of a Data Migration Plan
If you are planning to migrate your data center to a cloud environment, upgrade your database management system, perform server maintenance, or simply relocate data to a new data storage device, developing a data migration plan can simplify the process. Following a thorough, step-by-step plan that clearly outlines the different steps is important, especially when dealing with big data. While a data migration plan can be customized as per the business needs and objectives, generally, it consists of the following stages:
Data Assessment
Before the actual migration happens, it is vital to assess the source repository and understand the location and format of the data. In this discovery phase, the underlying dependencies and constraints in the data are identified. The data quality is evaluated by running audits and potential risks and security concerns that could arise during data migration are noted down.
Project Scoping
Once the underlying data has been thoroughly assessed, the scope of the migration project has to be defined. In this phase, a requirements specification is finalized for the resources required to carry out the migration. Organizations also decide on the data migration strategy to be used, i.e., big bang or trickle, and draft a budget and a schedule accordingly.
Data Backup
All of the data should be backed up in a secure location before the data transfer gets underway. In situations where data is corrupted, lost, or transferred incompletely during migration, the backup would allow the restoration of data to its original state. Public cloud services can be used to adequately backup data.
Building Migration Solution
This is the phase where the actual implementation happens. The data is extracted from the source system, converted into an appropriate format, and then transferred onto the target system using the mapping protocols already defined. During this step, initial tests on sample data are also conducted to set performance benchmarks for the actual data migration.
Testing & Production Migrations
Subsequent testing migrations are then performed with real-world data to ensure foolproof performance. The transfer process is fully refined until all exceptions are accounted for. Once the accuracy of the migrated data is ensured, approvals from the relevant stakeholders are collated and the production migration is executed.
Cleanup and Monitoring/Maintenance
As the data migration goes live, strategies are put into place to decommission the legacy system and set up auditing protocols to maintain the new system. Different data validation practices and performance monitoring tools are employed in this final stage.
Mitigating the Risk Factors in Data Migration
- Interference Risk: This problem is encountered when multiple users access an application program at the same time during the migration process. It could lead to a lack of access for other stakeholders if someone closes the program while the data transmission is happening.
- Solution: This could be avoided by discussing it beforehand in pre-migration planning. The organization could also plan a pilot run in a testing environment involving all stakeholders
- Data Loss: During the migration process, some of the data may not transfer from the legacy system to the target system due to a variety of reasons such as incompatible system formats, incomplete data transfer etcetera. It can be extremely costly to recover data and can, in some cases, lead to permanent loss of data.
- Solution: Using data reconciliation technique which is a data verification process in which data in the target system is compared with original source data to check if the number of records in both the versions match or not.
- Data Breach/Corruption: If data in the new system differs from that in the old system then it has become corrupted during the migration process. The presence of unrelated, missing, or anomalous data can also indicate data corruption.
- Solution: One way to prevent data corruption issues is by conducting data validation and testing to ensure that data from the legacy system has been correctly mapped onto the new system.
- Semantics Risks: Semantics-related exceptions can occur even though the data migration may have been completed smoothly. For instance, the contents of a column in a particular dataset in the old system could get copied into a different field in the new system. This is not a case of data corruption or loss but it could lead to major concerns for companies.
- Solution: Experts of semantic data in the company should be kept in the loop while planning test cases to identify and mitigate such inconsistencies. Resolution of this issue often requires manual work to draw comparisons between the two systems.
Difference between Data Migration, Data Integration, and Data Conversion
The two terms, data migration and data conversion are often used interchangeably. However, it is important to understand the difference between them.
Data migration, as established above, is the process of transferring data between different systems, formats, and locations.
Data conversion, meanwhile, refers to the transformation of data to a different format. It is used because legacy systems often have data stored in formats that need to be altered before the migration can happen. Therefore, data conversion is essentially a smaller step in the data migration process.
Data integration is another term that is used reciprocally with data migration. It is the process of bringing together data from multiple sources and creating a consolidated view of the data for analytical purposes. It is used in data warehousing and is considered a major step in the data management process.
Data Migration with Integrate.io
The global data migration market is exponentially growing and its projected growth by 2026 is nearly $23 billion. It is becoming extremely important for businesses to equip themselves with the right data migration tools and strategies. The Integrate.io toolkit offers all the cutting-edge tools that you need to perform smooth and secure data migration.
Are you ready to discover how the Integrate.io platform can help you with your data migration needs? Contact our team today to schedule a 7-day demo or pilot and see how we can help you reach your goals.